In the world of Machining, tool and die making, and CNC Operators, precision is paramount. A tradesperson’s work relies on exact measurements, attention to minute details and an array of specialized tools. One such tool that every machining tradesperson, especially newcomers to such trades, should consider having or even making given the opportunity is a Machinist 1-2-3 Block. This seemingly simple block serves as an indispensable tool for machinists, ensuring accuracy and efficiency in a variety of applications. In this article, we will explore what a machinist 1-2-3 Block is, what materials it is made from, some of the diverse uses and why it is an essential tool for someone in the machining trades, be it a General machinist, tool and die maker or a CNC programmer/operator.
What is a Machinist 1-2-3 Block?
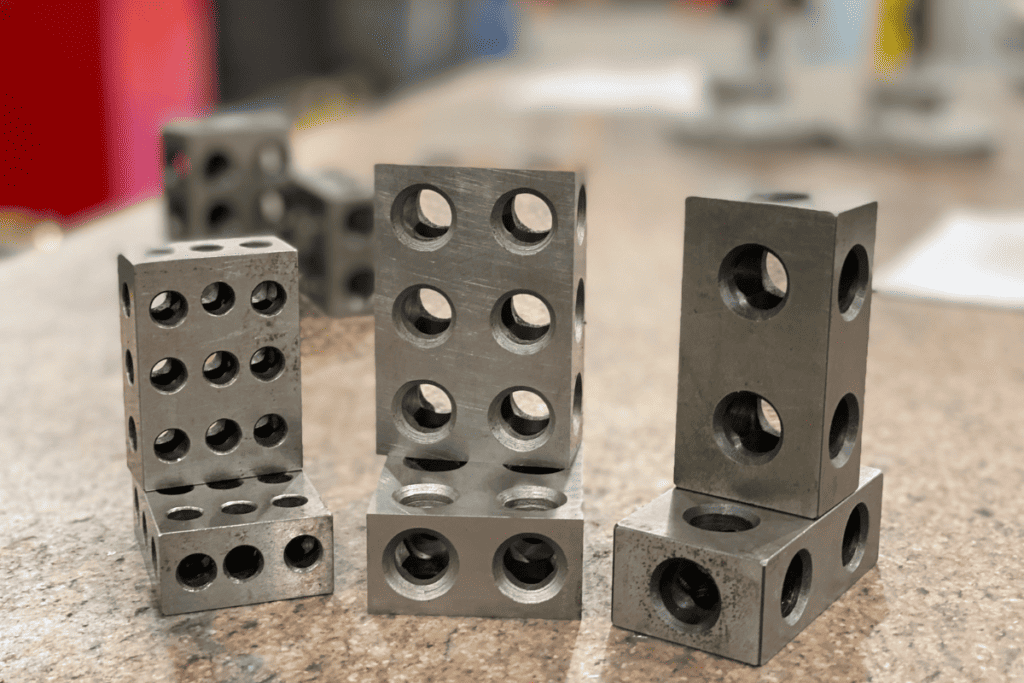
The Machinist 1-2-3 Block, often referred to simply as a “1-2-3 Block,” is a precisely machined and highly accurate rectangular block used in various machining, fabrication, and inspection tasks. It is named the “1-2-3 Block” because it typically has three distinct faces, with each face measuring 1 inch by 2 inches by 3 inches, providing machinists with a set of easily recognizable and standardized reference dimensions. It is very common for the tradesperson to make their own 1-2-3 block that will meet the specifications of their work environment. Tool and Die makers use their blocks for grinding work on a magnetic chuck, so they will leave most of the material on the block, yet a CNC operator will use the block for setting up machining fixtures, not needing them to be magnetized it is common to put a series of standard hold in the block to make them lighter. Having standardized holes on 1-2-3 blocks also will help you stack and use a drill rod or a pin in the blocks to attach the to each other if you need to build them up. Be aware that 1-2-3 blocks come in several sizes and that 1-2-3 is just a common set for a tradesperson to have of their own. Tooling shops will often have 2-4-6 and larger series if they are commonly used in the shop.
Material Composition
Machinist 1-2-3 Blocks are typically crafted from high-quality materials known for their dimensional stability and durability. Common materials used in their construction include:
Steel: Many 1-2-3 Blocks are made from hardened and ground steel, offering excellent resistance to wear and corrosion. These blocks are particularly favoured for their longevity and precision. They may have a shiny, polished finish, and their hardness makes them ideal for rigorous machining operations.
Cast Iron: Some 1-2-3 Blocks are made from cast iron, which is known for its stability and vibration-damping properties. Cast iron blocks are typically used for less demanding applications or when cost is a significant consideration. They are still reliable and precise tools, although they may be more susceptible to rust. Often, larger-sized blocks in a 2-4-6 inch series for maching setups are made from cast iron.
Granite: In select cases, you might come across 1-2-3 Blocks made from granite. Granite offers exceptional dimensional stability and resistance to temperature changes, making it ideal for precise measurement and inspection tasks. Granite blocks are less common but valuable for specialized applications.
The choice of material depends on the specific requirements of the task at hand. Each material offers its unique set of advantages, ensuring the 1-2-3 Block remains an invaluable tool for machinists.
Uses of the Machinist 1-2-3 Block
The Machinist 1-2-3 Block may seem unassuming, but its versatility and precision make it a crucial tool for a wide range of tasks in the machining industry. Here are some common uses for this indispensable tool:
Layout and Setup: Machinists use 1-2-3 Blocks as reference surfaces for laying out and setting up workpieces on milling machines, lathes, and other machining equipment. The flat and parallel faces of the block provide a stable base for accurate positioning and alignment.
Inspection: 1-2-3 Blocks are essential for measuring, calibrating, and inspecting parts. Their precision dimensions make them a reliable gauge for checking the accuracy of machined components, ensuring they meet the required specifications.
Height and Depth Measurement: When stacked or used individually, 1-2-3 Blocks serve as height and depth gauges. Machinists can precisely measure the height of workpieces or the depth of holes and slots by placing the block against them. This should only be done with the inspection grade block.
Squaring and Angular Measurement: Machinists often employ 1-2-3 Blocks in conjunction with other measuring tools, such as dial indicators and squares, to ensure that workpieces are square and at the correct angles. These blocks serve as reference surfaces during these alignment processes.
Support and Clamping: In certain situations, machinists use 1-2-3 Blocks as supports for workpieces during machining operations. They can also be employed as clamping devices to secure parts in place.
Reference Surfaces: The flat, parallel, and perpendicular surfaces of 1-2-3 Blocks provide precise reference surfaces for numerous machining operations. Machinists rely on these blocks to ensure the accuracy of their work and maintain tight tolerances.
Why New Machinists Need a Set of 1-2-3 Blocks
For new machinists, the Machinist 1-2-3 Block is a fundamental tool that provides several advantages, making it a wise investment for anyone starting out in the trade. Here are some compelling reasons why new machinists need a set of 1-2-3 Blocks:
Precision Training: Newcomers to machining need to develop a keen sense of precision and attention to detail. 1-2-3 Blocks are perfect tools for training in the art of accurate measurement and meticulous work. They offer a clear reference point for honing one’s skills.
Versatility: As detailed earlier, 1-2-3 Blocks are incredibly versatile. For beginners, this means that a single tool can serve multiple purposes, reducing the need for an extensive collection of specialized tools. It is an excellent starting point for a new machinist’s toolkit.
Cost-Effective Solution: Investing in a set of 1-2-3 Blocks is cost-effective. Their durability ensures they will last a long time, providing value for the money spent. New machinists can benefit from the wide range of tasks these blocks can perform without the need to buy numerous specialized tools initially.
Developing Measurement Skills: Accurate measurement is a cornerstone of machining. The 1-2-3 Block helps new machinists understand the importance of precision in the field. It serves as a tangible reference for measurement and calibration, allowing individuals to develop their measurement skills.
Alignment and Setup: Proper setup and alignment are critical to achieving high-quality machining results. New machinists can use 1-2-3 Blocks to learn how to position workpieces accurately, ensuring that their machining operations produce the desired outcomes.
Quality Control: For machinists, maintaining quality control is paramount. 1-2-3 Blocks play a key role in the inspection and quality control process. New machinists can use them to become familiar with these essential procedures early in their careers.
If you want to know more about how to become a Machinist, Click here
If you want to know how to become a Tool and Die Marker, Click Here.
Conclusion
The Machinist 1-2-3 Block may seem simple, but it is a cornerstone tool for anyone involved in the world of precision machining. From its versatile applications to the choice of materials and precision machining, these blocks provide an invaluable resource for new machinists. They offer a platform for learning and skill development and ensure the highest standards of quality in the machining industry. Every new machinist should consider adding a set of 1-2-3 Blocks to their toolkit to kickstart their journey towards becoming a skilled and proficient machinist.
You can get a set of Foller 1-2-3 blocks with a carrying case by CLICK HERE.


